Microsoft 70-410 Exam Questions
- Microsoft MCSA: Windows Server 2012 Certifications
- Microsoft Certified Solutions Expert MCSE Certifications
- Topic 1: Design Storage Spaces, Configure Basic And Dynamic Disks/ Add And Remove Features In Offline Images
- Topic 2: Optimize Resource Utilization By Using Features On Demand/ Plan For A Server Installation, Plan For Server Roles, Plan For A Server Upgrade
- Topic 3: Configure Server Core, Delegate Administration, , Deploy Roles On Remote Servers/ Migrate Roles From Previous Versions Of Windows Server
- Topic 4: Convert Server Core To/From Full GUI, Configure Services, Configure NIC Teaming/ Create And Mount Virtual Hard Disks (Vhds)
- Topic 5: Configure Storage Pools And Disk Pools, Create Storage Pools By Using Disk Enclosures/ Install And Configure Windows Powershell Desired State Configuration (DSC)/ Configure Master Boot Record (MBR) And GUID Partition Table (GPT) Disks
- Topic 6: Configure Servers For Day-To-Day Management Tasks/ Configure Printer Pooling, Configure Print Priorities
- Topic 7: Create And Configure Shares, Configure Share Permissions, Configure Offline Files/ Configure Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS)
- Topic 8: Configure NTFS Permissions, Configure Access-Based Enumeration (ABE)/ Configure NTFS Quotas, Create And Configure Work Folders
- Topic 9: Configure The Easy Print Print Driver, Configure Enterprise Print Management/ Configure Down-Level Server Management
- Topic 10: Configure Multi-Server Management, Configure Server Core/ Configure Printer Permissions
- Topic 11: Configure Windows Firewall, Manage Non-Domain Joined Servers/ Configure Servers For Remote Management/ Configure Print And Document Services
- Topic 12: Configure Synthetic And Legacy Virtual Network Adapters/ Configure Guest Integration Services/ Configure Pass-Through Disks, Manage Checkpoints
- Topic 13: Implement A Virtual Fibre Channel Adapter, Configure Storage Quality Of Service/ Configure Dynamic Memory, Configure Smart Paging
- Topic 14: Create And Configure Virtual Machine Storage/ Create And Configure Virtual Machine Settings/ Create And Configure Generation 1 And 2 Virtual Machines
- Topic 15: Configure And Use Enhanced Session Mode, Configure Remotefx/ Optimize Network Performance, Configure MAC Addresses
- Topic 16: Create Vhds And VHDX, Configure Differencing Drives, Modify Vhds/ Onfigure Hyper-V Virtual Switches
- Topic 17: Configure Network Isolation/ Configure NIC Teaming In Virtual Machines/ Create And Configure Virtual Networks
Free Microsoft 70-410 Exam Actual Questions
Note: Premium Questions for 70-410 were last updated On 01-01-1970 (see below)
You have an offline image of a server that runs Windows Server 2012 R2.
You need to enable Remote Desktop Services (RDS) on the server.
What should you use?
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. All client computer accounts are in an organizational unit (OU) named AllComputers. Client computers run either Windows 7 or Windows 8.
You create a Group Policy object (GPO) named GP1.
You link GP1 to the AllComputers OU.
You need to ensure that GP1 applies only to computers that have more than 8 GB of memory.
What should you configure?
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) filters allow you to dynamically determine the scope of Group Policy objects (GPOs) based on attributes of the target computer.
When a GPO that is linked to a WMI filter is applied on the target computer, the filter is evaluated on the target computer. If the WMI filter evaluates to false, the GPO is not applied (except if the client computer is running Windows Server, in which case the filter is ignored and the GPO is always applied). If the WMI filter evaluates to true, the GPO is applied. WMI filters, like GPOs, are stored on a per-domain basis. A WMI filter and the GPO it is linked to must be in the same domain.
References:
Training Guide: Installing and Configuring Windows Server 2012 R2: Chapter 10: Implementing Group Policy, p.470, 482
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj134176
WMI filtering using GPMC
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. You have a Group Policy object (GPO) named GP1 that is linked to the domain. GP1 contains a software restriction policy that blocks an application named App1.
You have a workgroup computer named Computer1 that runs Windows 8. A local Group Policy on Computer1 contains an application control policy that allows App1.
You join Computer1 to the domain.
You need to prevent App1 from running on Computer1.
What should you do?
AppLocker policies take precedence over policies generated by SRP on computers that are running an operating system that supports AppLocker.
AppLocker policies in the GPO are applied, and they supersede the policies generated by SRP in the GPO and local AppLocker policies or policies generated by SRP.
Your network contains a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. Server1 has the Hyper-V server role installed.
Server1 hosts four virtual machines named VM1, VM2, VM3, and VM4.
Server1 is configured as shown in the following table.
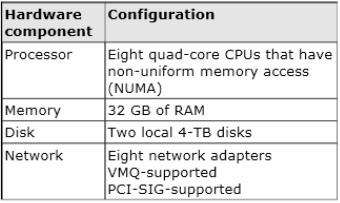
You need to ensure that VM1 can use more CPU time than the other virtual machines when the CPUs on Server1 are under a heavy load.
What should you configure?
B . Resource controls provide you with several ways to control the way that Hyper-V allocates resources to virtual machine. Resource control in used in the event where you need to adjust the computing resources of a virtual machine, you can reconfigure the resources to meet the changing needs. You can also specify resource controls to automate how resources are allocated to virtual machines.
References:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc766320(v=ws.10).aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh831410.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc742470.aspx
Exam Ref 70-410, Installing and Configuring Windows Server 2012 R2, Chapter 3: Configure Hyper-V, Objective 3.1: Create and Configure virtual machine settings, p.144
Training Guide: Installing and Configuring Windows Server 2012 R2: Chapter 7: Hyper-V Virtualization, Lesson 2: Deploying and configuring virtual machines, p.335
Your network contains a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. Server1 has the Hyper-V server role installed.
Server1 hosts four virtual machines named VM1, VM2, VM3, and VM4.
Server1 is configured as shown in the following table.
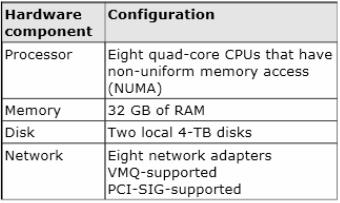
VM2 sends and receives large amounts of data over the network.
You need to ensure that the network traffic of VM2 bypasses the virtual switches of the parent partition.
What should you configure?
Single-root I/O virtualization -capable network adapters can be assigned directly to a virtual machine to maximize network throughput while minimizing network latency and the CPU overhead required for processing network traffic.
References: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc766320(v=ws.10).aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh831410.aspx
Exam Ref 70-410, Installing and Configuring Windows Server 2012 R2, Chapter 3: Configure Hyper-V, Objective 3.1: Create and Configure virtual machine settings, p.144
Training Guide: Installing and Configuring Windows Server 2012 R2: Chapter 7: Hyper-V Virtualization, Lesson 2: Deploying and configuring virtual machines, p.335
- Select Question Types you want
- Set your Desired Pass Percentage
- Allocate Time (Hours : Minutes)
- Create Multiple Practice tests with Limited Questions
- Customer Support
Currently there are no comments in this discussion, be the first to comment!