Free Microsoft AZ-104 Exam Dumps - Page 15
Hotspot
You have an Azure subscription that contains the virtual machines shown in the following table:
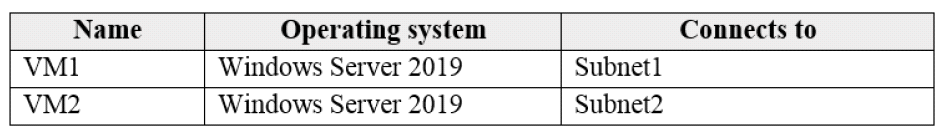
VM1 and VM2 use public IP addresses. From Windows Server 2019 on VM1 and VM2, you allow inbound Remote Desktop connections.
Subnet1 and Subnet2 are in a virtual network named VNET1.
The subscription contains two network security groups (NSGs) named NSG1 and NSG2. NSG1 uses only the default rules.
NSG2 uses the default rules and the following custom incoming rule:
Priority: 100
Name: Rule1
Port: 3389
Protocol: TCP
Source: Any
Destination: Any
Action: Allow
NSG1 is associated to Subnet1. NSG2 is associated to the network interface of VM2.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

References:
Hotspot
You have a virtual network named VNET1 that contains the subnets shown in the following table:
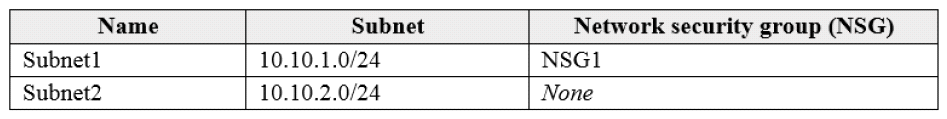
You have two Azure virtual machines that have the network configurations shown in the following table:
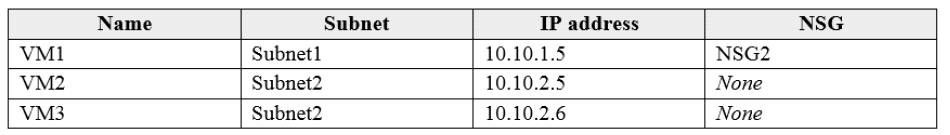
For NSG1, you create the inbound security rule shown in the following table:

For NSG2, you create the inbound security rule shown in the following table:

For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Box 1: Yes
The inbound security rule for NSG1 allows TCP port 1433 from 10.10.2.0/24 (or Subnet2 where VM2 and VM3
are located) to 10.10.1.0/24 (or Subnet1 where VM1 is located) while the inbound security rule for NSG2
blocks TCP port 1433 from 10.10.2.5 (or VM2) to 10.10.1.5 (or VM1). However, the NSG1 rule has a higher
priority (or lower value) than the NSG2 rule.
Box 2: Yes
No rule explicitly blocks communication from VM1. The default rules, which allow communication, are thus
applied.
Box 3: Yes
No rule explicitly blocks communication between VM2 and VM3 which are both on Subnet2. The default rules,
which allow communication, are thus applied.
Hotspot
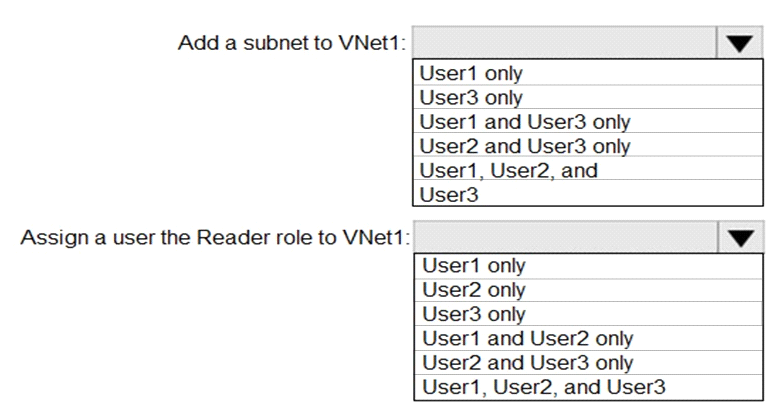
You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that contains a virtual network named VNet1.
You add the users in the following table.
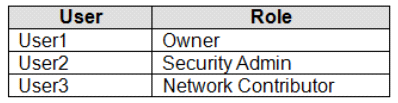
Which2? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Explanation
Hotspot
You have an Azure subscription named Subscroption1.
In Subscription1, you create an alert rule named Alert1.
The Alert1 action group is configured as shown in the following exhibit.
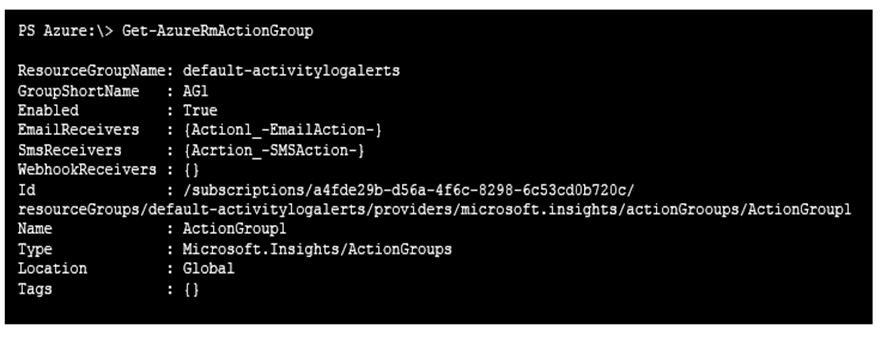
Alert1 alert criteria is triggered every minute.
Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement based on the information presented in the graphic.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Box 1: 60
One alert per minute will trigger one email per minute.
Box 2: 12
No more than 1 SMS every 5 minutes can be send, which equals 12 per hour.
Note: Rate limiting is a suspension of notifications that occurs when too many are sent to a particular phone number, email address or device. Rate limiting ensures that alerts are manageable and actionable.
The rate limit thresholds are:




References:
Hotspot
You have an Azure subscription.
You plan to use Azure Resource Manager templates to deploy 50 Azure virtual machines that will be part of the same availability set.
You need to ensure that as many virtual machines as possible are available if the fabric fails or during servicing.
How should you configure the template? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
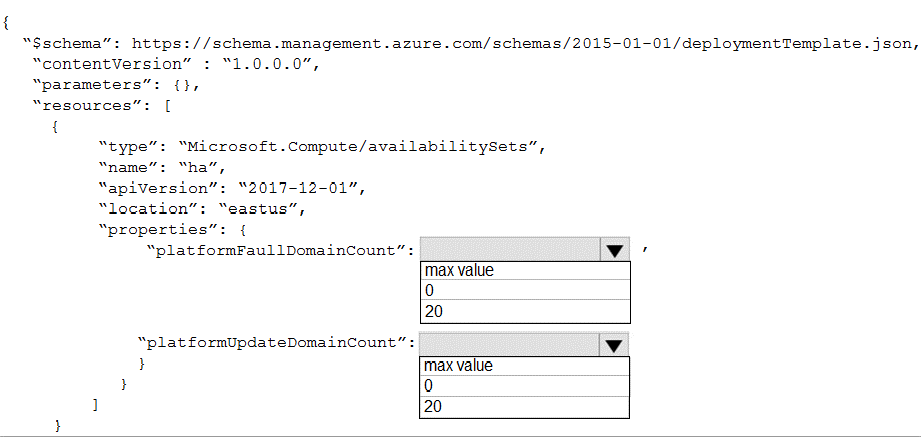
Box 1 = max value
Box 2 = 20
Explanation
Use max for platformFaultDomainCount
2 or 3 is max value, depending on which region you are in.
Use 20 for platformUpdateDomainCount
Increasing the update domain (platformUpdateDomainCount) helps with capacity and availability planning when the platform reboots nodes. A higher number for the pool (20 is max) means that fewer of their nodes in any given availability set would be rebooted at once.
References:
Hotspot
You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that contains the virtual networks in the following table.
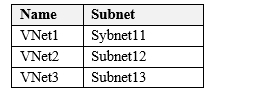
Subscripton1 contains the virtual machines in the following table.
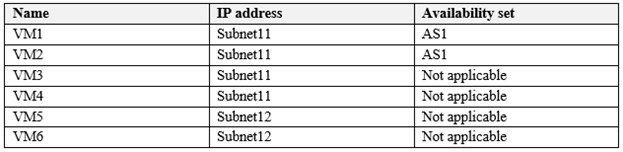
In Subscription1, you create a load balancer that has the following configurations:
Name: LB1
SKU: Basic
Type: Internal
Subnet: Subnet12
Virtual network: VNET1
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: each correct selection is worth one point.

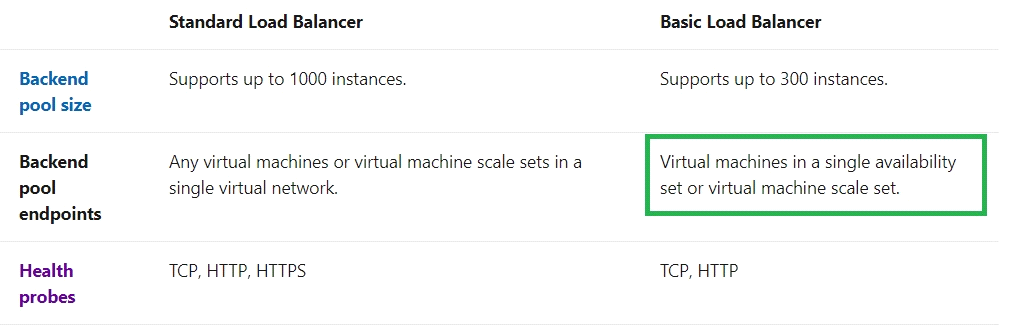
Statement 1 :Basic load balancer supports Virtual machine in a single Availability set or virtual machine scale set (VMSS) only . Hence this statement is correct.
Statement 2 :Basic load balancer supports Virtual machine in a single Availability set or virtual scale set only or one standalone VM. VM3 and VM4 are not part of any availability set or VMSS .Hence this statement is incorrect.
Statement 3 :Basic load balancer supports Virtual machine in a single Availability set or virtual scale set only or one standalone VM. VM5 and VM6 are not part of any availability set or VMSS .Hence this statement is incorrect.
References:
Hotspot
You have an Azure subscription.
You create the Azure Storage account shown in the following exhibit.
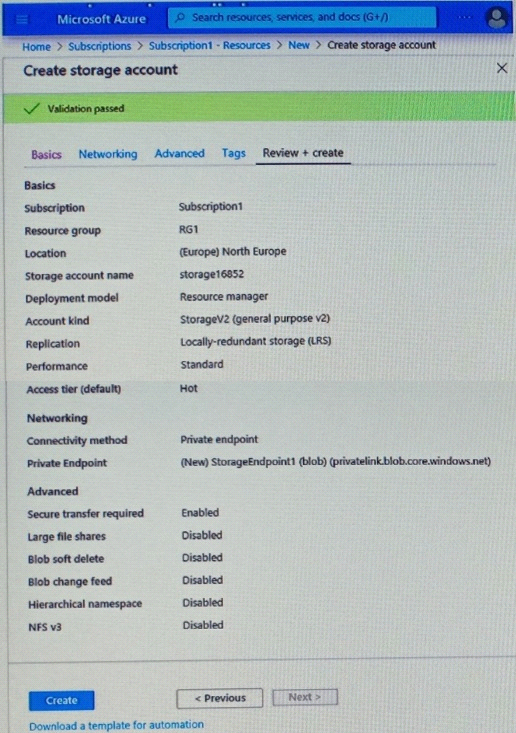
Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement based on the information presented in the graphic.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
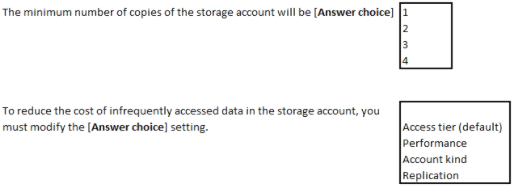
Box1:LRS will keep minimum three copies.
Box2:Changing the access tier from hot to cool will reduce the cost. In performance, standard is cheap.
In the Account kind, GPV2 is giving best price. Can be checked yourself using the pricing calculator on below link.
Hotspot
You plan to use Azure Network Watcher to perform the following tasks:
Task1: Identify a security rule that prevents a network packet from reaching an Azure virtual machine
Task2: Validate outbound connectivity from an Azure virtual machine to an external host
Which feature should you use for each task? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
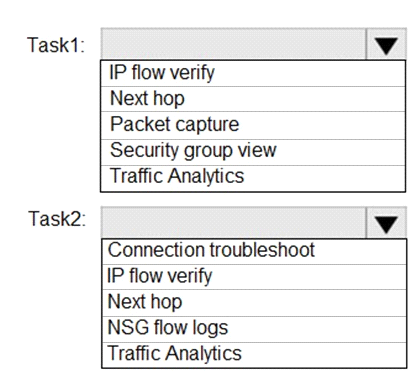
Task 1: IP flow verify
The IP flow verify capability enables you to specify a source and destination IPv4 address, port, protocol (TCP or UDP), and traffic direction (inbound or outbound). IP flow verify then tests the communication and informs you if the connection succeeds or fails. If the connection fails, IP flow verify tells you which security rule allowed or denied the communication, so that you can resolve the problem.
Task 2: Connection troubleshoot
The connection troubleshoot capability enables you to test a connection between a VM and another VM, an FQDN, a URI, or an IPv4 address. The test returns similar information returned when using the connection monitor capability, but tests the connection at a point in time, rather than monitoring it over time.
Hotspot
You have an Azure virtual machine named VM1 that connects to a virtual network named VNet1. VM1 has the following configurations:
Subnet: 10.0.0.0/24
Availability set: AVSet
Network security group (NSG): None
Private IP address: 10.0.0.4 (dynamic)
Public IP address: 40.90.219.6 (dynamic)
You deploy a standard, Internet-facing load balancer named slb1.
You need to configure slb1 to allow connectivity to VM1.
Which changes should you apply to VM1 as you configure slb1? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Box 1:Remove the public IP address from VM1
If the Public IP on VM1 is set to Dynamic, that means it is a Public IP with Basic SKU because Public IPs with Standard SKU have Static assignments by default, that cannot be changed. We cannot associate Basic SKUs IPs with Standard SKUs LBs. One cannot create a backend SLB pool if the VM to be associated has a Public IP. For Private IP it doesn't matter weather it is dynamic or static, still we can add the such VM into the SLB backend pool.
Box 2:Create and configure an NSG
Standard Load Balancer is built on the zero trust network security model at its core. Standard Load Balancer secure by default and is part of your virtual network. The virtual network is a private and isolated network. This means Standard Load Balancers and Standard Public IP addresses are closed to inbound flows unless opened by Network Security Groups. NSGs are used to explicitly permit allowed traffic. If you do not have an NSG on a subnet or NIC of your virtual machine resource, traffic is not allowed to reach this resource. To learn more about NSGs and how to apply them for your scenario, see Network Security Groups. Basic Load Balancer is open to the internet by default.
DragDrop
You have an Azure subscription that contains a storage account.
You have an on-premises server named Server1 that runs Window Server 2016. Server1 has 2 TB of data.
You need to transfer the data to the storage account by using the Azure Import/Export service.
In which order should you perform the actions? To answer, move all actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
NOTE: More than one order of answer choices is correct. You will receive credit for any of the correct orders you select.
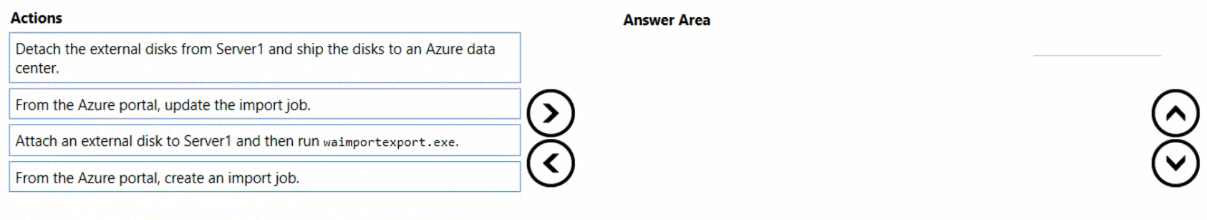















At a high level, an import job involves the following steps:
Step 1: Attach an external disk to Server1 and then run waimportexport.exe
Determine data to be imported, number of drives you need, destination blob location for your data in Azure storage.
Use the WAImportExport tool to copy data to disk drives. Encrypt the disk drives with BitLocker.
Step 2: From the Azure portal, create an import job.
Create an import job in your target storage account in Azure portal. Upload the drive journal files.
Step 3: Detach the external disks from Server1 and ship the disks to an Azure data center.
Provide the return address and carrier account number for shipping the drives back to you.
Ship the disk drives to the shipping address provided during job creation.
Step 4: From the Azure portal, update the import job
Update the delivery tracking number in the import job details and submit the import job.
The drives are received and processed at the Azure data center.
The drives are shipped using your carrier account to the return address provided in the import job.
References:

