CFA Institute Exam CFA-Level-II Topic 2 Question 54 Discussion
Topic #: 2
James Walker is the Chief Financial Officer for Lothar Corporation, a U .S . mining company that specializes in worldwide exploration for and excavation of precious metals. Lothar Corporation generally tries to maintain a debt-to-capital ratio of approximately 45% and has successfully done so for the past seven years. Due to the time lag between the discovery of an extractable vein of metal and the eventual sale of the excavated material, the company frequently must issue short-term debt to fund its operations. Issuing these one to six month notes sometimes pushes Lothar's debt to capital ratio above their long-term target, but the cash provided from the short-term financing is necessary to complete the majority of the company's mining projects.
Walker has estimated that extraction of silver deposits in southern Australia has eight months until project completion. However, funding for the project will run out in approximately six months. In order to cover the funding gap. Walker will have to issue short-term notes with a principal value of $1,275,000 at an unknown future interest rate. To mitigate the interest rate uncertainty, Walker has decided to enter into a forward rate agreement (FRA) based on LIBOR which currently has a term structure as shown in Exhibit 1.
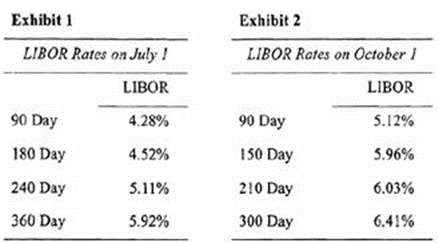
Three months after establishing the position in the forward rate agreement, LIBOR interest rates have shifted causing the value of Lothar's FRA . position to change as well. The new LIBOR term structure is shown in Exhibit 2.
While Walker is estimating the change in the value of the original FRA position, he receives a memo from the Chief Operating Officer of Lochar Corporation, Maria Steiner, informing him of a major delay in one of the company's South African mining projects. In the memo, Stciner states the following: "As usual, the project delay will require a short-term loan to cover funding shortage that will accompany the extra time until project completion. I have estimated that in 210 days, we will require a 90-day project loan in the amount of $2,350,000.1 would like you to establish another FRA position, this time with a contract rate of 6.95%."
Which of the following statements regarding the credit risk associated with Walker's original FRA contract three months after the inception of the contract is least accurate?
In forward markets, there is no clearinghouse. Forward contracts are between two private entities, and as such, rhe credit risk is borne by the part)* with a positive contract position. In Walker's case, since the contract has positive value three months after inception, he is exposed to the risk that the short position will be unable to make the required payment at the contract expiration. This problem could be alleviated through periodically marking the contract to market. Mark-to-market features are not common to ail forward contracts but can be included if so desired by the parties entering into the contract. (Study Session 16, LOS 58.d)
Currently there are no comments in this discussion, be the first to comment!