Arcitura Education Exam S90.20 Topic 1 Question 12 Discussion
Topic #: 1
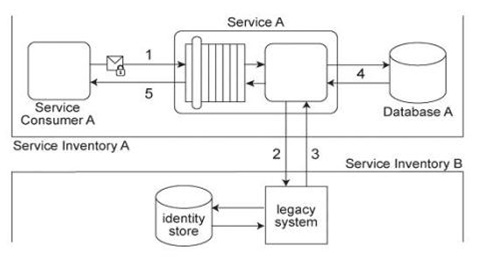
Service Consumer A submits a request message with security credentials to Service A (1). The identity store that Service A needs to use in order to authenticate the security credentials can only be accessed via a legacy system that resides in a different service inventory. Therefore, to authenticate Service Consumer A, Service A must first forward the security credentials to the legacy system (2). The legacy system then returns the requested identity to Service A (3). Service A authenticates Service Consumer A against the identity received from the legacy system. If the authentication is successful, Service A retrieves the requested data from Database A (4), and returns the data in a response message sent back to Service Consumer A (5). Service A belongs to Service Inventory A which further belongs to Security Domain A and the legacy system belongs to Service Inventory B which further belongs to Security Domain B .(The legacy system is encapsulated by other services within Service Inventory B, which are not shown in the diagram.) These two security domains trust each other. Communication between Service A and the legacy system is kept confidential using transport-layer security. It was recently discovered that a malicious attacker, posing as Service Consumer A, has been accessing Service A .An investigation revealed that these attacks occurred because security credentials supplied by Service Consumer A were transmitted in plaintext. Furthermore, vulnerabilities to replay attacks and malicious intermediaries have been detected. Which of the following statements describes a solution that can counter these types of attacks?
Also, list the industry standards required by the proposed solution.
Currently there are no comments in this discussion, be the first to comment!