AICPA Exam CPA-Financial Topic 3 Question 61 Discussion
Topic #: 3
There are multiple active markets for a financial asset with different observable market prices:
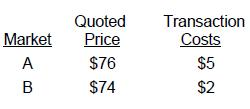
There is no principal market for the financial asset. What is the fair value of the asset?
Choice 'c' is correct. When there is no principal market, the price in the most advantageous market is the fair value measurement. Although transaction costs are not included in the fair value measurement, they are used to determine the most advantageous market, as follows:
Market A: Net Price = Quoted Price - Transaction Costs = $76 - 5 = $71
Market B: Net Price = Quoted Price - Transaction Costs = $74 - 2 = $72
Because the net price in Market B is higher than the net price in Market A, Market B is the most advantageous market and the quoted price in Market B ($74) is the fair value of the asset.
Choice 'a' is incorrect. This is the net price in Market A. Fair value does not include transaction costs.
Choice 'b' is incorrect. This is the net price in Market B. This net price indicates that Market B is the most advantageous market, but the net price is not the fair value because fair value does not include transaction costs.
Choice 'd' is incorrect. If Market A were the principal market for the asset, then this would be the fair value of the asset. However, because there is no principal market, the price in the most advantageous market (Market B) is the price of the asset.
Currently there are no comments in this discussion, be the first to comment!